Renewable Energy Mapping
There are a growing number of applications that demonstrate the use of satellite data in the renewable energy sector. Satellite data can in many cases better inform resource assessments, especially those done at a large spatial scale. For example, solar radiation can be measured from space and inform decision-making on where to put solar farms. In addition, more comprehensive environmental impact assessments can be conducted with satellite data. This ensures that investments in renewable energy or not only well informed but have limited impact on the natural environment. Among the mapping of renewable energy resources and generation, other applications include energy access mapping, electrification modelling and smart grid planning.
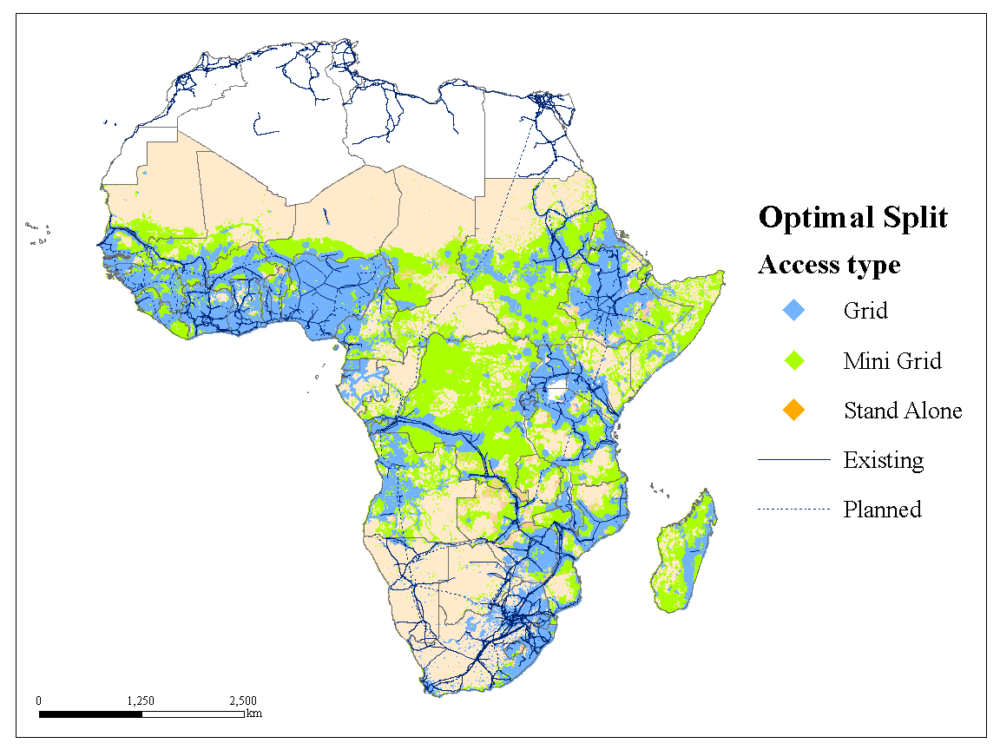
OnSSET is an open source, spatial electrification tool that provides technology and investment outlooks on expanding access through on grid, off-grid and mini-grid systems. Considering several data layers such as renewable energy potential, location of infrastructure (grid network, roads, power plants), OnSSET maps out the mix of technologies that are the most cost-efficient across the studied region to reach certain electricity access goals.1
Some recent demonstration projects by ESA have included Gridwatch, which was aimed to detect small, slow movements of transmission towers and the ground, Point 4 designed for vegetation monitoring and auditing, Sharper Shape designed for distribution and transmission asset management and ISSWind for offshore wind resource mapping.2
Related to renewable energy mapping is the mapping and estimation of carbon sequestration potential (carbon capture) by estimating ground biomass and seasonal productivity of forests and other ecosystems.
1) https://cleantechnica.com/2019/05/10/seeing-energy-from-space-5-tools-using-remote-sensing-to-improve-life-on-earth/
2) https://www.smart-energy.com/industry-sectors/data_analytics/satellite-data-to-support-the-renewables-transition/